Bone Marrow Edema: Everything You Need To Know

Bone marrow edema is an inflammatory process that usually occurs in the trabecular bone. In other words, it occurs in the inner, “spongy” component of bone. The causes range from trauma to degenerative diseases. It also sometimes occurs among those who begin to engage in strenuous physical activity after living a sedentary life.
The scientific journal Dolor, Investigación, Clínica y Terapéutica explains that this pathology is frequent in clinical practice of rheumatology. This is because there is greater use and availability of magnetic resonances as a diagnostic test. Therefore, it has become easier to identify this type of problem.
So, with all this in mind, what are the characteristics?
What is bone marrow edema?
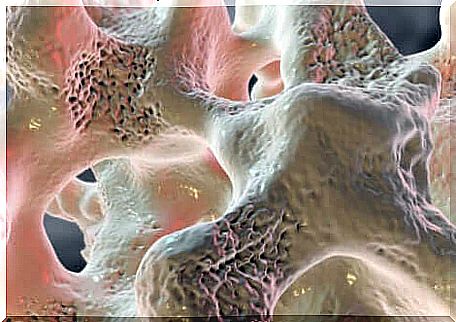
Simply put, we can say that bones consist of two things that are easy to distinguish between. One of them is the cortical bone, which is made of a hard and compact material that surrounds the outer shell of the skeleton. The other is the trabecular bone, a more “spongy” tissue made up of the inner skeletal material.
In the trabecular bone there are a large number of blood vessels since the bones must also be nourished. According to an article published by FASTA University of Argentina, an accumulation of fluid in the trabecular bone causes inflammation. This often happens because the blood vessels rupture and bleeding occurs inside the bone.
The origin may also lie in the accumulation of inflammatory fluid after an injury. Whatever the cause, it can be said that bone marrow edema is a kind of bruise inside the bone.
However, it is important to understand that this condition can also occur in cortical bones, although this is not so common. Furthermore, it is important to note that the characteristics vary according to the reversibility.
Thus, experts classify it into two major groups:
- Transient Bone Edema Syndrome (TBES) : This is a reversible inflammatory process that decreases with treatment and time.
- Osteonecrosis: This causes tissue death in bone tissue. Because of this, experts consider it an irreversible condition.
Why does bone marrow edema occur?
As might be expected, most cases of bone marrow edema are the result of injuries, falls, high physical exertion or overload during exercise or sports. Nevertheless, the Rheumatology of Hospital General de Elche warns us that in many cases the causes are not entirely clear.
Although the main trigger is usually a serious injury, micro-injuries that continue over time can also cause bone marrow edema. During a 10-kilometer race, for example, you hit the ground about 8,000 times. Therefore, this requires its own of the inner bone structure, as well as muscles and ligaments.
However, exercise is not the only trigger. Diseases such as osteoarthritis (degenerative arthritis), avascular necrosis (lack of blood supply), osteoporosis (osteoporosis) and complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) also promote the appearance of this inflammation. In short, anything that weakens the bone will make it more prone to fractures.
The symptoms of bone marrow edema
The clinical manifestations of bone marrow edema may vary from person to person, depending on the severity of the condition. According to information published in the journal Clinical Rheumatology, the main symptoms include the following:
- A local pain in the affected bone structure.
- Discomfort when using the injured leg. The pain increases when you exercise.
- When the injury is not treated quickly enough, the patient can feel the pain even when resting.
- In the most severe cases, one can experience discomfort during daily activities such as walking.
Due to the way it occurs, it may be easy to guess that bone marrow edema appears more frequently in the knees, metatarsals or heel bones. Nevertheless, the symptoms vary depending on the bone structure that is affected.
Diagnosis
This type of lesion is not visible with traditional radiography, so MRI is necessary. Studies also show that new techniques, such as Dual-Energy Computed Tomography (DET), which reconstructs images from material degradation, can be very useful tools in detecting bone marrow edema.
How is bone marrow edema treated?
According to professionals in traumatology, the treatment of bone marrow edema involves several phases:
- Rest is a crucial factor for beneficial recovery. It is important to use crutches to relieve acute symptoms. It is also important to reduce stress and strain on the leg for at least four weeks.
- Various medications can also be helpful. Examples of this can be painkillers to control pain, bisphosphonates, vitamins and other compounds to increase bone density or iloprost for vasodilation.
- After the initial medical stages, it is advisable to continue the improvement with the help of physiotherapy. This can include magnetic therapy, thermotherapy, muscle relaxation, water training and other techniques.
In the most severe cases, surgery may be necessary. It is possible to perform a spinal cord decompression by using several perforations to drain the fluid from the bone.
Preventive measures
As the popular saying goes, ” prevention is better than cure “. We should not put more strain on our bodies than is necessary. In the face of extreme physical activity, it is also important that there is a trainer who controls our training.
Furthermore, if you experience discomfort after walking, running or engaging in any other activity, you should see your doctor. Whether it is bone marrow edema, fracture or sprain, you need to get an early diagnosis to get treatment in time and prevent complications.